Network Architecture Review
Overview
A network architecture review is a critical process that ensures a network's design is aligned with an organization's needs, providing scalability, performance, and security. The review involves assessing the current architecture, identifying potential issues, and recommending improvements. Below are the detailed steps for conducting a comprehensive network architecture review
Our Methodology
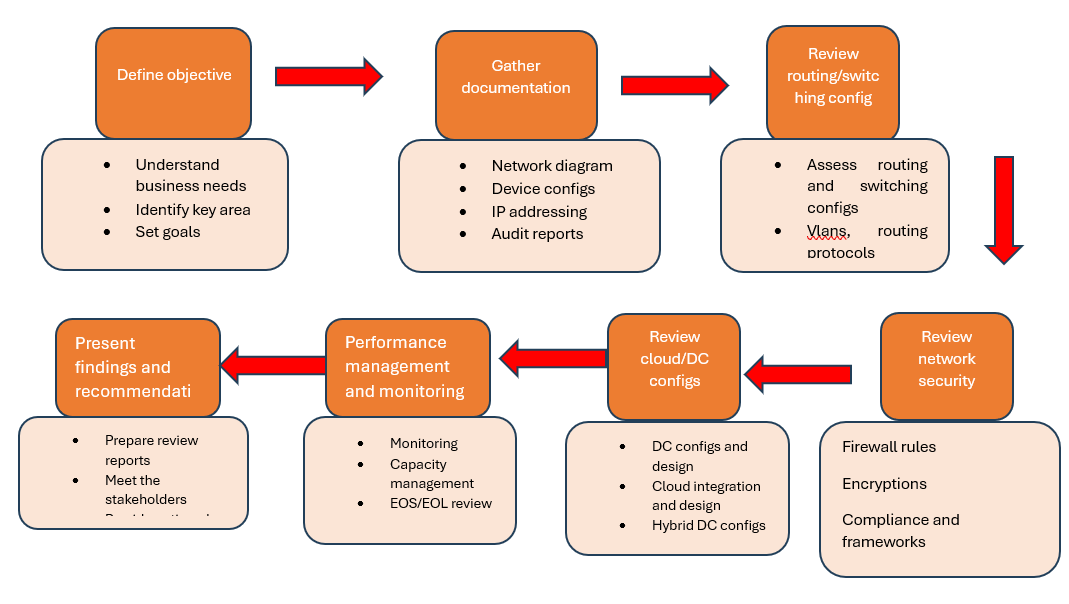
Define objectives and scope
• Understand Business Requirements: Meet with stakeholders to understand the organization's goals, such as performance, security, scalability, or compliance.
• Identify Key Focus Areas: Determine the specific areas of the network to review (e.g., data centers, WAN, LAN, cloud integration, or security policies).
• Set Review Goals: Clearly define the outcomes of the review (e.g., improving performance, enhancing security, or planning for future growth).
Gather Documentation and Information
• Collect Network Diagrams: Gather up-to-date network diagrams that outline the current architecture, including physical and logical topologies.
• Obtain Device Configurations: Collect configuration files from key devices such as routers, switches, firewalls, and load balancers.
• Review Network Policies: Analyze network security policies, routing tables, access control lists (ACLs), and quality of service (QoS) rules.
• Document IP Addressing Scheme: Ensure the IP addressing plan is clear and includes details on subnets, VLANs, and addressing strategy.
• Gather Performance Metrics: Obtain historical data on network performance, including bandwidth usage, latency, packet loss, and throughput.
• Audit Security Measures: Review security features such as firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and encryption protocols.
Assess Network Topology and Design
• Evaluate Physical and Logical Design: Assess the network's physical layout (e.g., cabling, hardware placement) and logical architecture (e.g., IP addressing, subnets, VLANs).
• Check Network Redundancy: Verify that there are sufficient redundant paths and failover mechanisms (e.g., backup links, dual-homed devices) to prevent single points of failure.
• Assess Network Segmentation: Ensure that the network is appropriately segmented to isolate traffic (e.g., separating guest networks, data centers, or critical applications).
• Evaluate Scalability: Review the network's ability to scale, considering bandwidth capacity, IP addressing space, and the ease of adding new devices or locations.
Review Routing and Switching Configurations
• Assess Routing Protocols: Examine routing protocols in use (e.g., OSPF, BGP, EIGRP) for efficiency, scalability, and redundancy.
• Check Routing Tables: Verify the accuracy and efficiency of routing tables, looking for routing loops, suboptimal routes, or unnecessary static routes.
• Evaluate VLAN Configuration: Ensure that VLANs are properly configured for traffic segmentation, performance, and security.
• Analyze QoS Policies: Review Quality of Service (QoS) configurations to ensure that critical traffic (e.g., VoIP, video) is prioritized and delivered without delay.
Review Network Security
Review Network Security
• Firewall Rules and ACLs: Examine firewall configurations and access control lists (ACLs) to ensure they provide adequate protection without overcomplicating access.
• Intrusion Detection/Prevention (IDS/IPS): Evaluate the effectiveness of IDS/IPS solutions in detecting and mitigating threats.
• Encryption Protocols: Ensure that sensitive data is encrypted both at rest and in transit (e.g., IPSec, SSL/TLS, VPN).
• Authentication and Access Control: Review the use of authentication protocols (e.g., RADIUS, TACACS+) and ensure role-based access control (RBAC) is in place to limit access to critical systems.
• Compliance with Security Standards: Ensure the network meets compliance requirements (e.g., PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR) based on the organization’s industry.
Assess Cloud and Data Center Integration
• Evaluate Cloud Networking: If the organization uses cloud services, ensure the network supports secure and efficient communication between on-premise and cloud environments (e.g., AWS, Azure).
• Review Data Center Architecture: For data centers, examine high availability (HA) and disaster recovery (DR) setups, ensuring redundancy, load balancing, and backup procedures are in place.
• Cloud Security: Check how data is protected during transfers to and from the cloud, reviewing encryption, VPNs, and security policies for cloud-based resources.
Review Network Management and Monitoring
• Network Monitoring Tools: Assess the tools in use for real-time monitoring, fault detection, and performance analysis (e.g., SolarWinds, PRTG, Nagios).
• Review Logging and Alerting: Ensure that logs are collected from key devices (e.g., firewalls, routers) and that appropriate alerts are configured for abnormal activity.
• Analyze Network Documentation: Verify that all network configurations, policies, and topologies are properly documented and kept up to date.
• Automated Network Management: Review any automation tools (e.g., Ansible, Cisco DNA Center) used for network provisioning and management, ensuring they are properly configured.
Present Findings and Recommendations
• Prepare a Review Report: Document the findings from the review, including network performance metrics, identified gaps, and proposed solutions.
• Meet with Stakeholders: Present the review findings to key stakeholders, including IT teams, business leaders, and decision-makers, ensuring alignment on the next steps.
• Provide Next Steps: Clearly outline the immediate actions required, as well as any long-term strategies for maintaining a robust network architecture.
Head Office - USA
16192 COASTAL HIGHWAY LEWES, DELAWARE 19958
business@techsiagus.com
Regional office - Dubai - UAE
business@techsiagus.com
Regional office - Pakistan
business@techsiagus.com

