Security Audits and Assessments
Overview
The process of conducting a security audit involves several structured steps designed to assess an organization's adherence to security policies, standards, and regulations. The goal is to identify gaps in compliance, evaluate the effectiveness of security controls, and provide recommendations for improvement. Here are the key steps involved:
Our Methodology
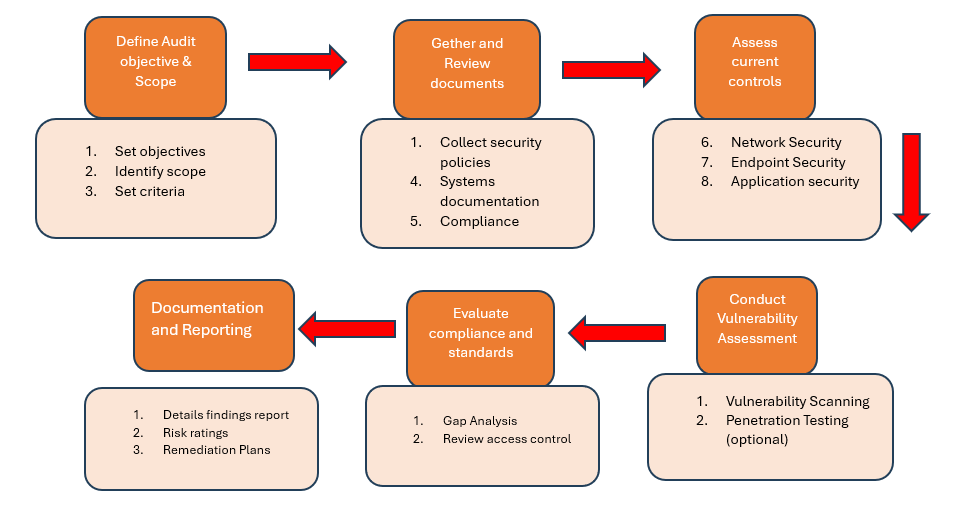
Define Audit Objectives and Scope
• Set clear objectives: Determine the purpose of the audit, such as compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), evaluation of internal policies, or risk management.
• Identify scope: Define the boundaries of the audit, including which systems, networks, data, applications, and departments will be assessed.
• Set criteria: Determine which standards or frameworks will be used (e.g., ISO 27001, NIST, PCI-DSS).
Assess Current Security Controls
• Technical controls: Evaluate technical controls such as firewalls, antivirus solutions, IDS/IPS systems, access controls, encryption, and patch management.
• Administrative controls: Review policies, procedures, security awareness training, and user access reviews.
• Physical controls: Inspect physical security measures, such as surveillance, locks, badges, and access to data centers.
Conduct Vulnerability Scanning and Testing
• Vulnerability scanning: Use automated tools to scan systems, networks, and applications for known vulnerabilities.
• Penetration testing (optional): Perform simulated attacks to test the organization’s defenses and identify exploitable vulnerabilities.
Evaluate Compliance with Standards
• Gap analysis: Compare the organization’s current practices against the applicable standards (e.g., ISO 27001, NIST, PCI-DSS) to identify any compliance gaps.
• Review access controls: Ensure that user access is properly managed, with the principle of least privilege applied.
• Incident response capabilities: Verify that incident detection and response mechanisms are in place and functioning.
Analyze Risk and Prioritize Findings
• Risk assessment: Analyze the identified vulnerabilities and gaps in security controls to determine the potential impact and likelihood of exploitation.
• Prioritize findings: Use a risk matrix to categorize and prioritize vulnerabilities based on their criticality, helping focus on the most pressing issues first.
Create a Remediation Plan
• Develop action plans: Establish a detailed remediation plan with timelines and assign responsible parties for each corrective action.
• Set deadlines: Prioritize the most critical issues and establish deadlines for addressing vulnerabilities based on their severity.
• Allocate resources: Ensure that necessary resources (budget, personnel, tools) are available to carry out the remediation efforts.
Head Office - USA
16192 COASTAL HIGHWAY LEWES, DELAWARE 19958
business@techsiagus.com
Regional office - Dubai - UAE
business@techsiagus.com
Regional office - Pakistan
business@techsiagus.com

